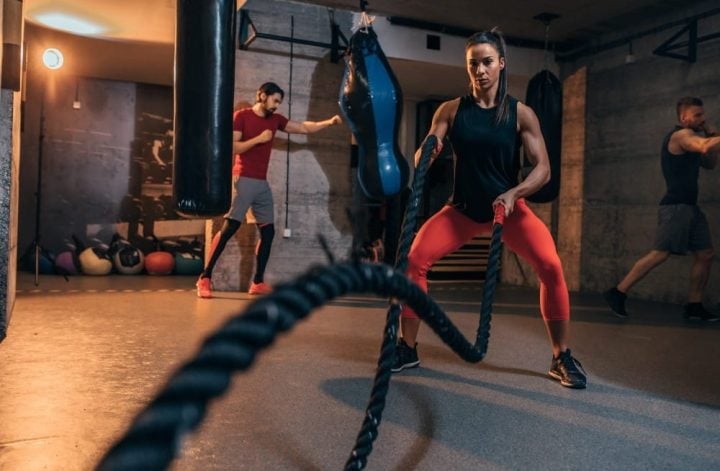
The importance and benefits of training
We know that staying active is one of the best ways to keep our bodies healthy. But did you know that it can also improve your general well-being and your quality of life? Regular physical activity can relieve stress, anxiety, depression and anger. Do you know what “good feeling” you feel after being active? Imagine it as a happiness pill with no side effects. Most people feel better over time when physical activity becomes an integral part of their lives.
It keeps you healthy and in good physical shape.
Without regular activity, the body slowly loses its strength, endurance and ability to function properly. It’s like the old saying, “Man doesn’t stop playing because he ages, he ages because he stops playing.” Exercise increases muscle strength, which, in turn, increases your ability to perform other physical activities.
Spending too much time sitting and other sedentary activities can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. A study has shown that adults who watch more than 4 hours of television a day have an 80% higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
Being more active can help you do the following:
- Lower blood pressure
- Increase good cholesterol levels
- Improves blood circulation (circulation)
- Keep the weight under control
- Avoid loss of bone mass which can cause osteoporosis
- Gain flexibility
- Improve cardiovascular capacity
- Increase muscle mass
- Training can help you live longer.
It is true that 70 is the new 60, but only if you are in good health. Physically active, healthy-weight people live about seven years longer than those who are not active and obese. And the important part is that these extra years are generally healthier years. Staying active delays or prevents chronic diseases and conditions associated with aging. As a result, active adults maintain their quality of life and independence for longer.
Here are some of the benefits you can get from regular physical activity:
- Helps you quit smoking and live tobacco-free.
- Increase the energy level to do more.
- It helps you control stress and tension.
- It promotes a positive attitude and outlook.
- It helps you sleep faster and deeper.
- Improves image and self-confidence.
- It will help you spend more time outdoors.
Move more, gradually more intensely and sit less. You don’t have to make big changes in your life to see the benefits. Start by incorporating more activity into your day, step by step.
What if I am recovering from a heart attack or stroke?
Some people are afraid to exercise after a heart attack. However, regular physical activity can reduce your chances of having another heart attack. If you have had a heart attack or stroke, talk to your doctor before you start exercising to make sure you are following a safe and effective physical activity program.
It is not necessary to do them every day; the variety helps keep the body healthy and fit, and makes exercise interesting. You can do a wide variety of exercises to make your physical activity routine fun. There are many different types of exercise that can improve strength, endurance, flexibility, and balance. For example, practicing yoga can improve your balance, strength and flexibility. Many lower body strength training exercises will also improve your balance. Weight training offers a wide range of benefits for the body such as weight loss, muscle or strength gains and allows athletes to physically prepare for certain sports.
The importance of working with flexibility
Flexibility exercises stretch the muscles and help maintain the flexibility of the body. These exercises may not improve your endurance, but flexibility gives you more freedom of movement for other exercises, as well as for your daily activities. A flexible muscle is a strong muscle. Working on the flexibility of a muscle increases its potential for strength. It can also help you avoid discomfort when you are in tight spaces for a long time (such as a long meeting or an airplane flight).
When should I stretch?
The best time to do flexibility exercises is when the muscles are already warm, so that you can stretch them more without tension or pain. If you’re only doing stretching exercises, start by walking for a few minutes to warm up your muscles. If you are doing resistance or strength exercises, stretch afterwards, not before.
How long should it last?
It is a good idea to do each exercise 3 to 5 times during each stretching session. Always stretch slowly and gently to the desired position, as long as it is comfortable and painless. Do what works best for you. If you are not used to the stretch, hold the stretch for about 10 seconds. The more you stretch, the easier it will be. Over time, you can comfortably hold each stretch for 30 seconds.
Tips for safe stretching:
Relax and breathe normally while stretching. Then stretch by exhaling slowly through your mouth. Count to 10 slowly or for 10 to 30 seconds. Breathe normally while stretching.
A stretch should always be smooth and slow, never sudden or in motion. This can cause muscle tension and injury. Hold the stretch for 10-30 seconds and repeat each stretch 3-5 times. Remember to breathe normally with each stretch.
As you become more flexible, try to stretch more with each exercise. It is normal for mild pain to occur during a stretch. More severe, very annoying pain, or joint pain means you have to stop because you are stretching too much. Always keep your joints slightly bent, never “fixed” in an upright position. This can cause injury.
Training to gain muscle mass requires a regular increase in intensity.
To progress in training to gain muscle mass, it is essential to progress regularly, that is to say to increase the weights used during training. During training, the muscles must reach the limit to establish a training stimulus to which the muscle adapts. Thanks to this adaptation, the muscle grows and becomes stronger to better withstand the effort the next time. This effect is called super compensation. It may be helpful to keep a training journal. This can record the number of sets, the weights used and the “sensations” felt during training. With the training log, you can see the progress very well (permanent increase in strength) and you can make intermittent adjustments to the training plan. When training to gain muscle mass, the focus should be on functional exercises, that is, performing basic exercises regularly that work large muscle groups instead of forming small muscle groups. in isolation. Beginners can compose their training to gain full muscle mass from basic exercises. However, the advanced level sessions should also be composed of at least 40% to 60% of functional movements such as bench press, squat and deadlift.
When training to gain muscle mass, it is essential to work the legs to the same extent as the rest of the body. This prevents optical and orthopedic imbalances. In addition, demanding leg exercises benefit the whole body. For example, squats also strengthen the back and abdominal muscles. This type of training not only builds muscles, but also improves all coordination skills and prepares you for the challenges of everyday life.
Training to gain muscle mass is a matter of patience
Muscle mass does not increase overnight. Results are only achieved in the medium term when the same value is given to the three components (training, nutrition and regeneration), so it takes commitment and patience.
The good news is that, in principle, all bodies are capable of creating quality muscle mass. With disciplined training, even beginners can gain up to 2-5 lbs of muscle per month, sometimes more depending on genetics and the work done.
Training plan to gain muscle mass
Non-professional athletes often lack the plan necessary for specific training to gain muscle mass. Despite the fact that the first months of training are generally successful, the so-called stagnation is soon reached. Training to gain muscle mass stagnates after a few weeks if the effort and caloric intake is not increased.
If a person continues to train like this, in the medium term, he remains below his possibilities. If the muscle groups are generally not trained in a balanced way and the relation between the phases of training and regeneration is not adequate, this lack of method leads to ineffectiveness.
For this reason, for beginners and experienced athletes, it is necessary to develop a training plan to gain muscle mass and to follow it consistently for several weeks.
Intensity techniques for training to earn muscle mass
The progress of training to gain muscle mass slows down over time, which is completely normal. However, you not only have to settle for stagnant weights and optical evolution, but you can overcome it with new training stimuli. Here are some intensity techniques that can be flexibly incorporated into training to gain muscle mass and bring success and variety to your training routine.
DROP-SETS
This intensity technique is one of the most popular in training to gain muscle mass. In a reduction series, you train to muscle failure; the weight is then reduced as quickly as possible and the training continues immediately. This cycle can be repeated several times per exercise.
NEGATIVE REPETITION
In negative repetitions, only the return movement of an exercise is performed with help, while a training partner helps in the muscle relaxation phase (the so-called eccentric movement). This phase is therefore carried out more slowly.
Example: In the bench press, the training partner helps to push the barbell to fully extend the arms. Then the bar is lowered unaided, retaining the heavy load throughout the eccentric movement.
Negative repetitions are very useful in training to gain muscle mass, since they require eccentric force, that is, the ability of muscles to slow down movements. They also improve intramuscular coordination and can be the first step in learning how to perform many exercises with body weight, such as pull-ups.
SUPER-SETS
In the so-called super-sets or superseries, two exercises are always performed in a row, without a break. These can combine two opposite muscle groups, called antagonists, but it is also possible to work together on the same part of the body.
In conclusion
Physical and / or sporting activity is beneficial at any age. It decreases overall mortality from any cause and in doing so increases life expectancy. Training reduces the cardiovascular risk, the thromboembolic risk, plays a decisive role in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, in the onset of colon and breast cancer, in the genesis of cognitive and depressive disorders. Having more muscle mass helps keep your metabolism faster and prevents many injuries. Adopting an active lifestyle or maintaining it brings only benefits to all human beings!